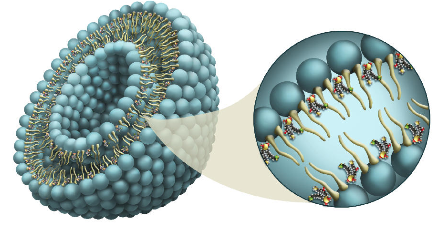
Liposomal latanoprost
Lipolat is an extended release drug delivery solution that is a ground breaking development in nanomedicine for ophthalmology.
Liposomal latanoprost has completed a pilot Phase 2a trial in the US for glaucoma indication.
A clinical study now is underway for its application in treating eyebags (steaoblepharon). A first of its kind method to eliminate unwanted fat in the periorbital and orbital region for both cosmetic and medical indications.
Publications
-
Sustained Drug Release in Nanomedicine: A Long-Acting Nanocarrier-Based Formulation for Glaucoma
Natarajan JV, et al. ACS Nano 2014 -
Nanomedicine for glaucoma: liposomes provide sustained release of latanoprost in the eye
Natarajan JV, et al. International Journal of Nanomedicine 2012 -
Sustained release of an anti-glaucoma drug: demonstration of efficacy of a liposomal formulation in the rabbit eye
Natarajan JV, et al. PLoS One 2011 -
Patient acceptance and attitude toward an alternative method of subconjunctival injection for the medical treatment of glaucoma
Chong RS, et al. J Glauc 2013
About Glaucoma
Glaucoma is the leading cause of irreversible blindness worldwide. Intraocular pressure (IOP) is the major risk factor for glaucoma. Medical therapy with topical eyedrops to lower the IOP remains as the first line treatment to prevent progressive visual field loss and blindness.[1] As the number of elderly in the world rapidly increases, glaucoma morbidity will rise. It has been estimated that glaucoma will be the most common cause of blindness in the world this century with almost 70 million cases of glaucoma worldwide.[2] This figure has very important public health implications for a condition which causes irreversible blindness, that typically affects the working population.
Medical treatment with eyedrops is often lifelong. Like any chronic treatment, eyedrops require patient adherence as well as correct application. Unfortunately many patients have trouble using eyedrops and applying them correctly in the eye at the correct time. A consequence of poor patient adherence is treatment failure and a poor outcome from disease progression.[3] It is estimated that at least 10% of blindness is directly attributed to poor patient adherence to prescribed medications.[4]
Here at Peregrine, we recognize and understand the challenges faced by the ophthalmologist and their patients. Our goal is to provide solutions to improve glaucoma management.
References
- Quigley HA, Broman AT. Br J Ophthalmol 2006; 90: 262-7.
- Foster PJ, et al. Arch Ophthalmol. 2000;118:1105-11.
- Robin AL, et al. Am J Ophthal. 2007;144:533-40.
- Tsai JC, et al. J of Glaucoma. 2003;12:393-8.
Pipeline
Liposomal delivery systems for other classes of anti-glaucoma drugs are currently being developed.